Accounting Equation Explained Definition & Examples

Assets represent the ability your business has to provide goods and services. Or in other words, it includes all things of value that are used to perform activities such as production and sales. Any change to a liability or ownership claim necessitates the performance of analysis with the same structure. Thus, ABC & Co. has $17.5 billion of claims against its $17.5 billion of assets. Get instant access to lessons taught by experienced private equity pros and bulge bracket investment bankers including financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel Modeling. Apple performs $3,500 of app development services for iPhone 13 users, receives $1,500 from customers, and bills the remaining balance on the account ($2,000).
Double entry bookkeeping system
That’s why you’re better off starting with double-entry bookkeeping, even if you don’t do much reporting beyond a standard profit and loss statement. Owner’s equity is the residual interest or amount that assets exceed liabilities. It also represents the amount of paid-in capital and retained earnings as a result of doing business for profit. Now, these changes in the accounting equation get recorded into the business’ financial books through double-entry bookkeeping.
4: The Basic Accounting Equation
The balance of the total assets after considering all of the above transactions amounts to $36,450. It is equal to the combined balance of total liabilities of $20,600 and capital of $15,850 (a total of https://www.bookstime.com/ $36,450). For example, an increase in an asset account can be matched by an equal increase to a related liability or shareholder’s equity account such that the accounting equation stays in balance.
Examples of the Accounting Equation

Since Speakers, Inc. doesn’t have $500,000 in cash to pay for a building, it must take out a loan. Speakers, Inc. purchases a $500,000 building by paying $100,000 in cash and taking out a $400,000 mortgage. This business transaction decreases assets by the $100,000 of cash disbursed, increases assets by the new $500,000 building, and increases liabilities by the new $400,000 mortgage. As you can see, assets equal the sum of liabilities and owner’s equity.
- We think of economic entities as any organization or business in the financial world.
- Now that we have a basic understanding of the equation, let’s take a look at each accounting equation component starting with the assets.
- The accounting equation helps to assess whether the business transactions carried out by the company are being accurately reflected in its books and accounts.
- The accounting equation is the most fundamental concept in double-entry bookkeeping.
- In this example, we will see how this accounting equation will transform once we consider the effects of transactions from the first month of Laura’s business.
- The shareholders’ equity number is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities.
- Over 1.8 million professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more.
- Shareholders’ equity comes from corporations dividing their ownership into stock shares.
- For example, if a company becomes bankrupt, its assets are sold and these funds are used to settle its debts first.
- Any change to a liability or ownership claim necessitates the performance of analysis with the same structure.
- This arrangement is used to highlight the creditors instead of the owners.
Most sole proprietors aren’t going to know the knowledge or understanding of how to break down the equity sections (OC, OD, R, and E) like this unless they have a finance background. Still, you’ll likely see this equation pop up time and time again. Still, let’s dive into the differences between the two so that you can understand how each might affect your bookkeeping process. If you want to know more about accounting errors and how to spot them, we recommend reading Common Accounting Errors – A Practical Guide With Examples. For starters, it doesn’t provide investors or other interested third parties with an analysis of how well the business is operating.
- On the other hand, equity refers to shareholder’s or owner’s equity, which is how much the shareholder or owner has staked into the company.
- The owner’s equity is the share the owner has on these assets, such as personal investments or drawings.
- An owner has the right to take money or other assets for personal use.
- For small businesses, knowing how the accounting equation works can help you better understand financial statements, along with how bookkeepers do their jobs.
The combined balance of liabilities and capital is also at $50,000. These are some simple examples, but even the most complicated transactions can be recorded in a similar way. Essentially, the representation equates all uses of capital (assets) to all sources of capital, where debt capital leads to liabilities and equity capital leads to shareholders’ equity.
Revenues & Expenses in the Accounting Equation
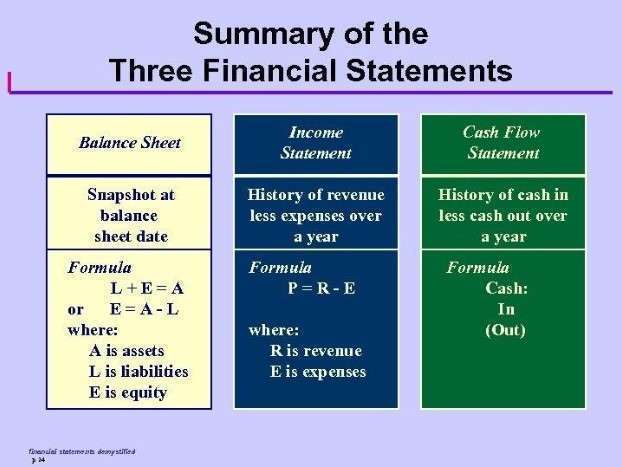
However, due to the fact that accounting is kept on a historical basis, the equity is typically not the net worth of the organization. The accounting equation is fundamental the accounting equation is usually expressed as to the double-entry bookkeeping practice. Some common examples of tangibles include property, plant and equipment (PP&E), and supplies found in the office.
